|
Achievements - Stage III
3D scanning for decorative objects

click to play
Automatic detection of 3D trajectories with the laser sensor
For technical details, please see:  SYROCO 2009 Paper (PDF) SYROCO 2009 Paper (PDF)

click to play
CNC milling of digitized decorative parts with complex surfaces
 
Left Small soldier (raw stock: wood); Right: Caesar model (raw stock: brass)
Scanning raw stock mounted on the rotary axis of CNC milling machine
In the figure below it is shown a raw stock made of wood, mounted on the rotary axis of the CNC machine.
The part was scanned with the robot looking inside the milling machine, using the rotary axis as a device for showing the part to the 3D sensor.
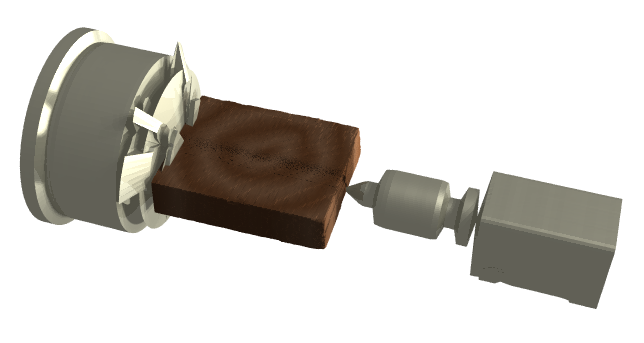
The figure was rendered using POV-Ray, from 3D data resulted from laser scanning.
Scanning parts mounted in this way has the following applications:
- Milling process optimization and automation:
- The exact size of raw stock do not need to be entered manually by the operator
- Also, the exact shape of the stock is acquired, optimizing the milling process for each raw part
- CNC alignment operations can be performed automatically
- It is possible to generate milling toolpaths with collision avoidance
- The time required for milling unique parts will be much lower
- Inline quality control for parts obtained by CNC milling
- The part can be inspected in place, right after milling, without requiring moving the part to a dedicated inspection equipment
- From the inspection results it is possible to determine compensation factors for the milling machine, such as succesive parts should be milled with tighter tolerances.
|

